tree in bud radiology assistant
Pus mucus or inflammatory exudate centrilobular bronchioles. Typical findings of BAC on HRCT include a solitary nodule or mass 43 focal or diffuse consolidation 30 or.

An Algorithmic Approach To The Interpretation Of Diffuse Lung Disease On Chest Ct Imaging Chest
Lymphadenopathy in left hilus right hilus and paratracheal 1-2-3 sign.
. 1 those with a tree-in-bud appearance and 2 those with ill-defined centrilobular nodules of GGA without a tree-in-bud appearance. The tree-in-bud pattern was first used as a descriptor by Im et al. Tools Share Abstract The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs.
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. 1 From the Department of Radiology University of Vienna Waehringer Guertel 18-20 A-1090 Vienna Austria. Received November 11 1999.
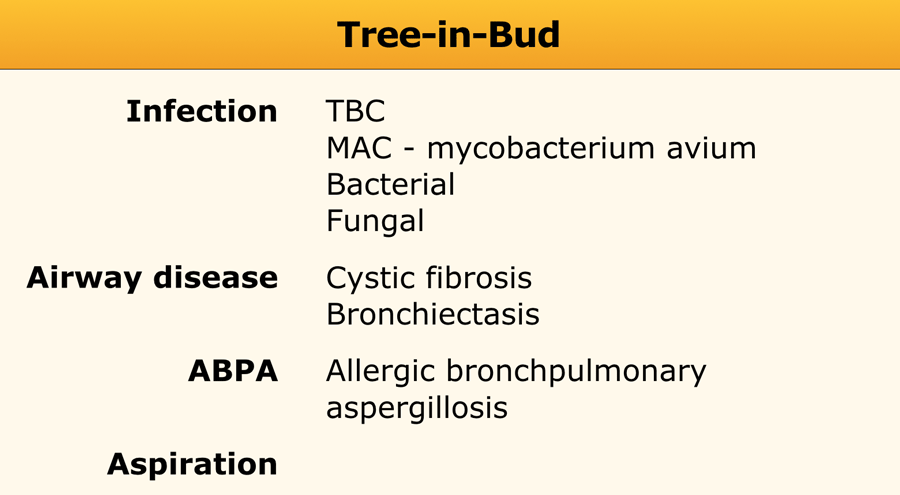
The differential for this finding includes malignant and inflammatory etiologies either. Tree-in-bud appearance represents dilated and fluid-filled ie. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
The tree-in-bud sign is a nonspecific imaging finding that implies impaction within bronchioles the smallest airway passages in the lung. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1996. Another important entity that can produce the tree-in-bud pattern is bronchioalveolar carcinoma BAC 1.
Frequency and significance on thin section CT. 3 found that the tree-in-bud pattern was seen in 256 of the CT scans in patients with bronchiectasis. Identification and evaluation of centrilobular opacities on high-resolution CT.
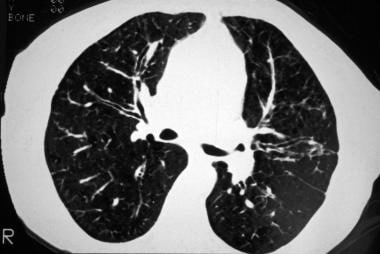
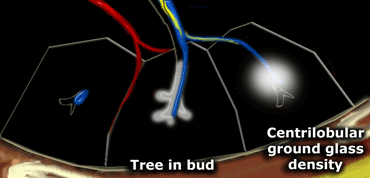
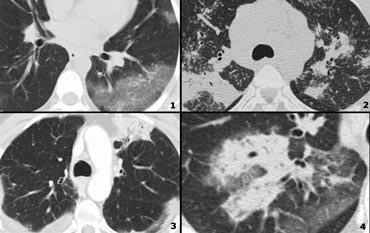
It consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber that originate from a. Medline Gruden JF Webb WR. Sourcewwwradiologyassistantnl 23K11 Description Tree-in-budIn centrilobular nodules the recognition of tree-in-bud is of value for narrowing the differential diagnosis.
However diseased bronchioles can be seen. Tree-in-bud refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery and associated with abnormalities of the larger airways. To describe the appearance of the endobronchial spread of mycobacterial tuberculosis.
Tree-in-bud pattern was first described for endobronchial spread of mycobacterium tuberculosis1 It is a CT scan finding of chest with visibility of small airways. Address correspondence to the author e-mail. The Tree-in-Bud Sign.
Tree-in-bud almost always indicates the presence of. These findings most likely represents pulmonary TB or MAC despite negative induced sputum specimens. Tree-in-bud describes the appearance of an irregular and often nodular branching structure most easily identified in the lung periphery.
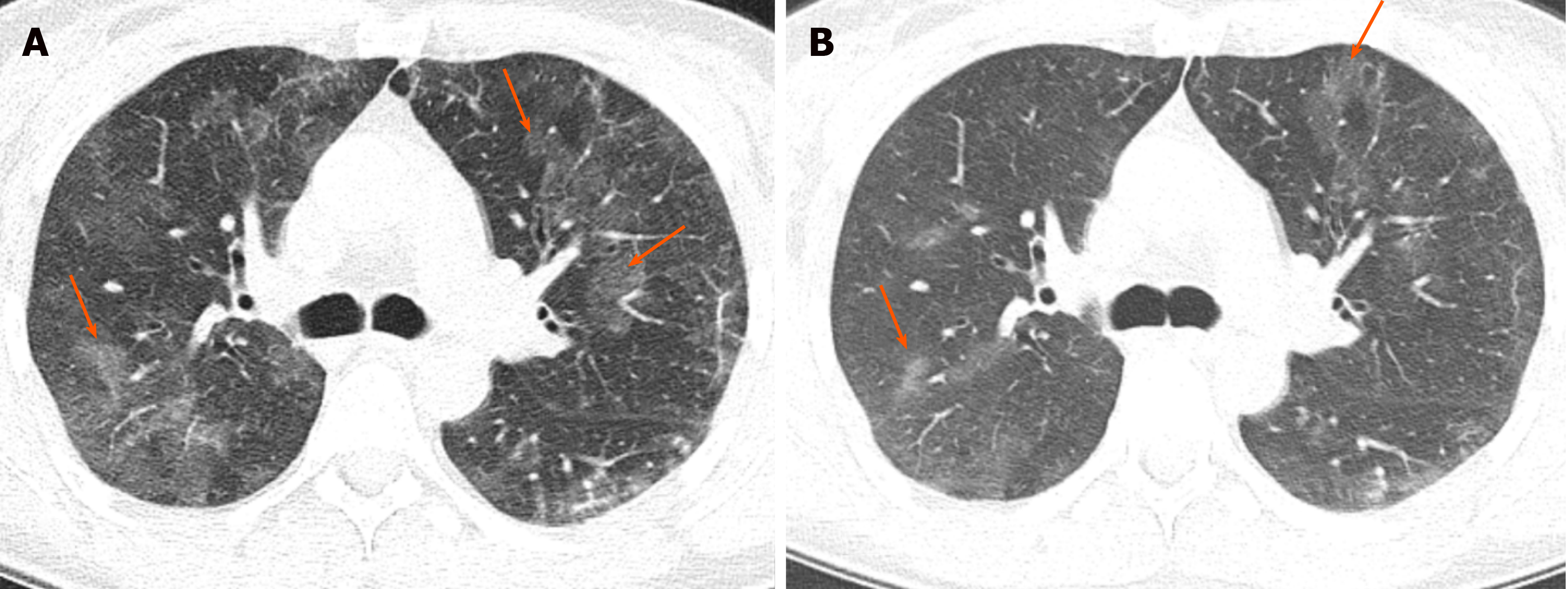
In radiology the tree-in-bud sign is a finding on a CT scan that indicates some degree of airway obstruction. Tree-in-bud pattern seen on high-resolution CT HRCT indicates dilatation of bronchioles and their filling by mucus pus or fluid. The centrilobular nodules were divided into two patterns.
Revision received and accepted May 22 2000. Endobronchial spread of infection TB MAC any bacterial bronchopneumonia Airway disease associated with infection cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis less often an airway disease associated primarily with mucus retention allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis asthmaDiagnosis Radiology. Chest x-ray in a 60 year old patient of Asian extraction demonstrates faint reticulonodular opacities.
The tree-in-bud appearance was characterised by well-defined centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation that were connected to linear and branching opacities. Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery and associated with abnormalities of the larger airways. Along subpleural surface and fissures along interlobular septa and the peribronchovascular bundle.
Tree-in-bud TIB is a radiologic pattern seen on high-resolution chest CT reflecting bronchiolar mucoid impaction occasionally with additional involvement of adjacent alveoli. Small nodules in a perilymphatic distribution ie. The tree-in-bud sign indicates bronchiolar luminal impaction with mucus pus or fluid causing normally invisible peripheral airways to become visible 80.
Semin Ultrasound CT MR 1995. CT confims numerous centrilobular nodules with opacified distal bronchioles tree-in-bud sign and bronchiectasis. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of TIB opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with TIB opacities.
Abnormal tree-in-bud bronchioles can be distinguished from normal centrilobular bronchioles by their more irregular appearance lack of tapering or knobbybulbous appearance at the tip of their branches. Bronchiolitis and bronchiolectasis are nonspecific inflammatory. Its microbiologic significance has not been systematically evaluated.
Upper and middle zone predominance. Revision requested December 10. Tree in bud opacification refers to a sign on chest CT where small centrilobular nodules and corresponding small branches simulate the appearance of the end of a branch belonging to a tree that is in bud.
Normal lobular bronchioles 1 mm in diameter cannot be seen on CT scans which can only show bronchi more than 2 mm in diameter. Tree-in-bud refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery and associated with abnormalities of the larger airways. This pattern is manifested by luminal filling of contiguous branching segments of bronchioles seen in bronchiolar disease.

Scielo Brasil Padroes Tomograficos Das Doencas Intersticiais Pulmonares Difusas Com Correlacao Clinica E Patologica Padroes Tomograficos Das Doencas Intersticiais Pulmonares Difusas Com Correlacao Clinica E Patologica
The Radiology Assistant Hrct Basic Interpretation

Learningradiology Lung Abscess Pulmonary Lunges Pulmonary X Ray
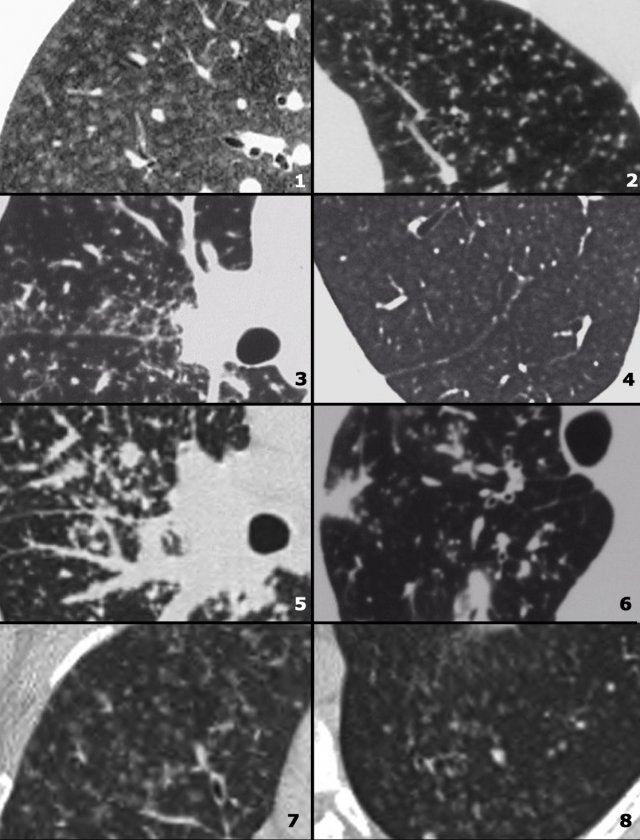
The Radiology Assistant Hrct Common Diagnoses

Basics Of Chest X Ray Dr Sheetu Singh Assistant Professor Ppt Download
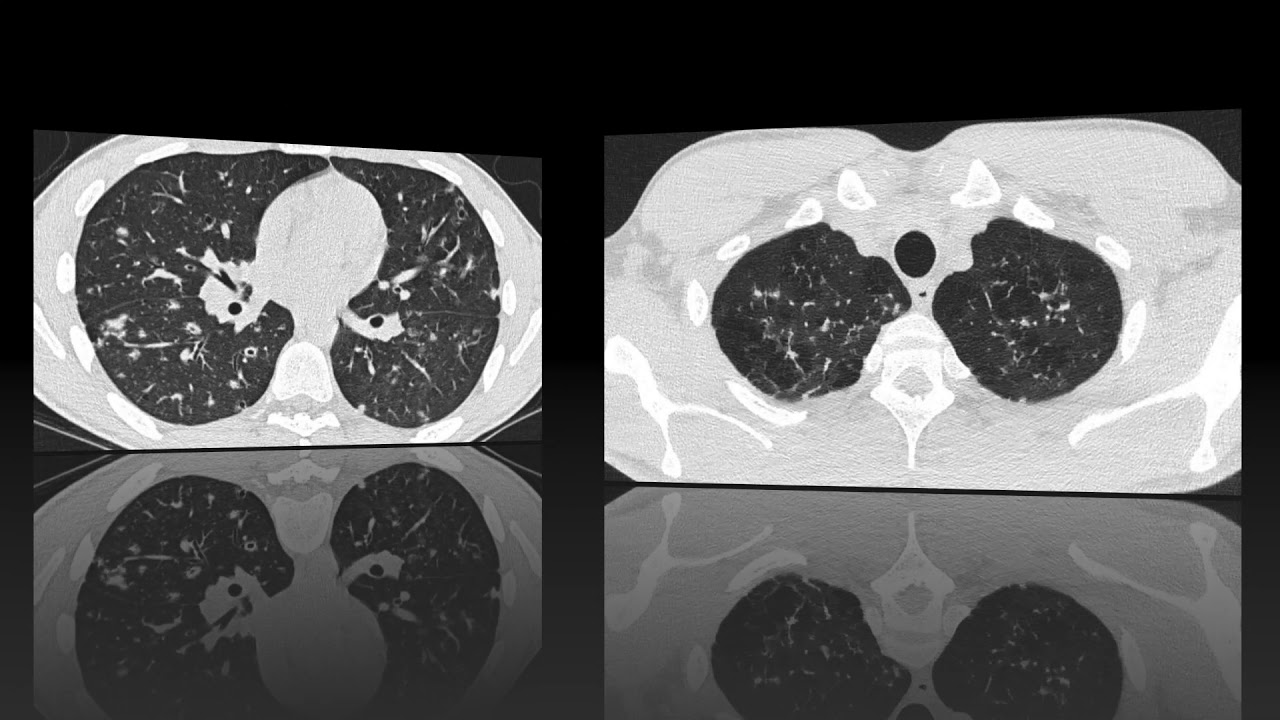
The Radiology Assistant Hrct Common Diagnoses
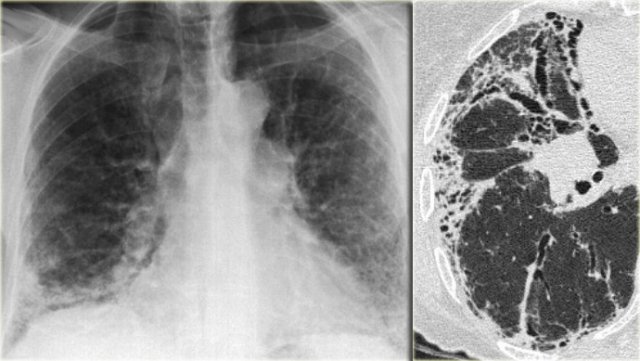
The Radiology Assistant Hrct Common Diagnoses

Csfoma Peritoneal Cerebrospinal Fluid Pseudocyst Csf Shunt Complication Xray X Ray Student Medical Radiology Imaging Radiology Radiologic Technology
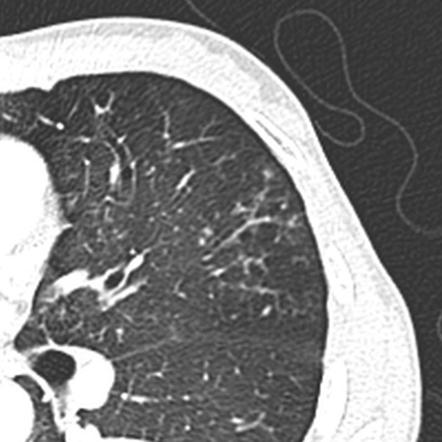
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Reverse 3 And 3 Sign Coarctation Abstract Artwork Antonio Mora Artwork Artwork
The Radiology Assistant Hrct Basic Interpretation
Which High Resolution Ct Hrct Findings Are Associated With A Diagnosis Of Bronchial Asthma

Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Chronic Airspace Disease Review Of The Causes And Key Computed Tomography Findings